Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
in Children and Adolescents

What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) is the commonest chronic health condition in the world affecting over 500 million people globally with another similar number probably undiagnosed or with pre-diabetes from young children to elderly adults.
T2D affects how your body turns food into energy. When you have type 2 diabetes, your body doesn't make or use insulin the way it should.
Insulin is a hormone secreted from the pancreas that helps your body use glucose for energy.
Insulin is like a “key” that unlocks a “metabolic gate” or channel into every cell of the body to allow glucose from your digested food to enter the cell and do all its amazing things with the body’s metabolism and energy pathways.

Without insulin one develops diabetes which is characterised by high blood glucose or sugar levels. As per the international guidelines if your fasting blood glucose is above 7 mmol/L or is above 11.0 mmol/L 2 hrs after a meal or a formal glucose tolerance test generally confirms you have diabetes.
The HbA1c test is now being used as a screening and diagnostic tool in diagnosing diabetes. It is an indirect but reasonably accurate diagnostic measure in adolescents and adults of diabetes. A HbA1c greater than 5.7% to 6.4% means you are likely to have pre-diabetes and a HbA1c equal to and greater than 6.5 % is diagnostic of diabetes.
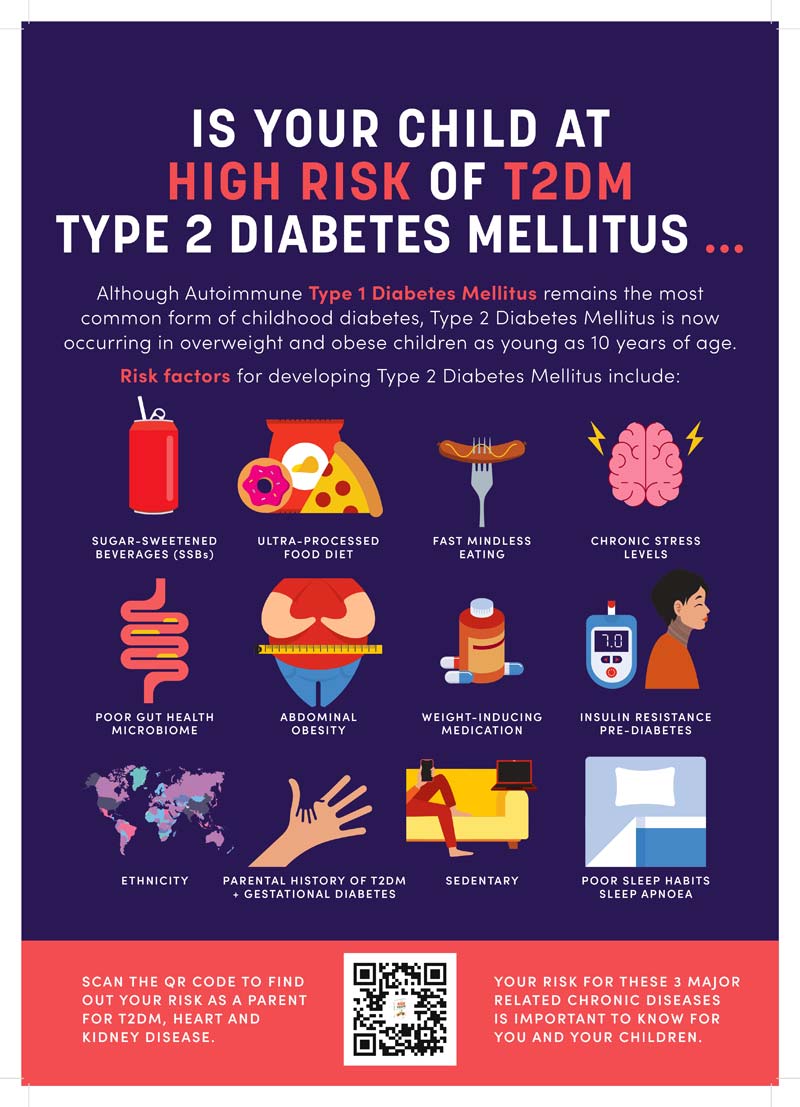
Who is at risk for type 2 diabetes?
Some people are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes than others. These include people who:
- Are overweight or obese, especially in those who are having rapid weight gain
- Have a family history of type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes
- Are of certain ethnic groups, such as Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander, South Pacific Islander, Maori, Central Asian including Chinese, Filipino, Indian and Pakistani, Mediterranean or Middle Eastern - see International Diabetes Federation World Diabetes Atlas
- Have certain health conditions, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Have signs of Insulin resistance with the dark velvety smooth rash on the neck or under the armpits or in joint skin creases called acanthosis nigricans
- Are physically inactive with excessive screen time
- Have chronic stress or mental illness or a history of Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
Can I prevent type 2 diabetes?
Yes. Type 2 diabetes can be totally prevented and even reversed in some individuals especially during the initial stages after diagnosis. These include:
- Maintaining a healthier weight but be aware we are all genetically different and not everyone is meant to be thin!
- Being overweight and mentally and physically fit is fine and can be associated with being healthy!
- Focus of small daily micro changes in your daily habits – small steps taken every day lead to big changes eventually- find a supportive friend to support your healthy journey and be accountable to each other for those days it is too cold or you had a bad day at work and don’t feel like going for your daily early morning walk or bike ride!
- Remember you cannot outrun an unhealthy highly processed take-away fake diet!
- Practice slow mindful-eating so you eat till you are satisfied, not full! Employ the 20 min rule to finish main meals and eat around the dinner table together as a family! Mindful eating will give you the same JOY from your food but eat less calories! What a DOUBLE BONUS!
- Eating a healthy diet of whole fresh fibre-filled foods, especially fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains and lean meats e.g. the Mediterranean diet has scientifically proven health benefits
- Focus on a good intake of low glycaemic-index whole foods
- Getting regular physical activity with huffy puffy movement and resistance training to build up your general cardio-vascular fitness and skeletal muscle mass and strength.
- Avoiding sugary drinks of all sorts! But now and then is Ok – you are only human!
- Quitting smoking and reducing your alcohol intake!
- Managing chronic stress and mental illness through mindfulness and meditation and social connection
- Finally practice Dr Gary’s 5 Qs!
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition in which cells in your body do not respond normally to insulin. This means that glucose cannot enter the cells and be used for energy. Insulin resistance is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
How can I know if I am at risk for type 2 diabetes?
You can take a diabetes risk calculator to estimate your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The Diabetes Australia diabetes risk calculator and the Heart Foundation cardiovascular disease risk calculator are two examples of these calculators.
I recommend all adults, especially parents, check one of these validated disease risk calculators including the Health Direct chronic disease risk calculator, which also includes risk for kidney disease.
How can I prevent type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents?
The best way to prevent type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents is to make healthy lifestyle changes. These changes include:
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular physical activity
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Avoiding sugary drinks
How is type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents different from type 1 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents is a much more aggressive disease than type 1 diabetes. This is because children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes are more likely to develop serious complications, such as kidney disease and retinopathy.
What are the complications of type 2 diabetes?
The complications of type 2 diabetes can affect many parts of the body, including the eyes, kidneys, heart, and blood vessels. Some of the most common complications include:
- Kidney disease: Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure in Australia.
- Retinopathy: Diabetes can damage the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. This can lead to vision loss.
- Heart disease: Diabetes is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
- Neuropathy: Diabetes can damage nerves, which can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the hands and feet.
- Gum disease: Diabetes can increase the risk of gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss.
How can I prevent the complications of type 2 diabetes?
The best way to prevent the complications of type 2 diabetes is to manage your blood sugar levels well. This means following a healthy diet, getting regular physical activity, and taking medication as prescribed by your doctor. Keeping your HbA1c test in the 6.5 to < 7.0% range has been shown to be associated very small risk of diabetes complications.
I hope this poster is helpful. Please let me know if you have any other questions.
How can mindfulness help prevent type 2 diabetes?
Mindfulness is the practice of paying attention to the present moment without judgment. It can help you to reduce stress, improve your mood, and make healthier choices.
There are many different ways to practice mindfulness. Some common techniques include:
- Meditation: Meditation is a practice of sitting quietly and focusing on your breath.
- Yoga: Yoga is a practice of physical postures and breathing exercises.
- Mindful eating: Mindful eating is the practice of paying attention to the food you are eating, from the moment you take it in your hand to the moment you swallow it.
Mindfulness can help you to reduce stress by helping you to become more aware of your thoughts and feelings. When you are mindful, you are less likely to react to stress in a negative way.
Mindfulness can also help you to make healthier choices. When you are mindful, you are more likely to pay attention to your hunger and fullness cues. You are also more likely to choose foods that are good for you.
How can I manage chronic stress and mental illness?
If you are struggling with chronic stress or mental illness, it is important to seek professional help. There are many different treatments available, including therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Therapy can help you to learn how to manage your stress and cope with your emotions. Medication can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. Lifestyle changes, such as exercise, yoga, and mindfulness, can also help to improve your mental health.
If you are concerned about your child's mental health, it is important to talk to your doctor. They can help you to assess your child's needs and make sure they get the right treatment.
By making these changes, you can help your child stay healthy and prevent type 2 diabetes.